You’ve probably heard about the importance of core muscles and doing exercises to develop them. In this way Pilates is an excellent option.
So why is the core so important to our overall health?
Core muscles play a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and physical ability. They are a group of muscles located in the abdomen, lower back, and pelvis that work together to provide stability and support for the spine and pelvis.
Here are some reasons why core muscles are important:
Better posture
A strong core can help you maintain good posture and alignment, which can reduce strain on your back, neck, and shoulders.
Improved balance and stability
The core muscles are responsible for keeping your body stable and balanced. A strong core can help prevent falls and injuries, especially as you age.
Enhanced athletic performance
The core muscles are involved in nearly every movement you make, from lifting weights to running to throwing a ball. A strong core can improve your overall athleticism and help you perform better in your chosen sport or activity.
Reduced risk of back pain
The core muscles support the spine and can help prevent and alleviate back pain.
Improved digestion and breathing
The core muscles are also involved in the process of breathing and digestion, as they help to support the organs and facilitate movement in the digestive tract.
Many people when they think of their core only associate it with their abdominal muscles. However, these aren’t the only muscles that work together as part of your core.
As you can see in the image below, the core muscles refer to a group of muscles located in the midsection of the body, including the abdominals, back, hips, and pelvic floor. These muscles play a crucial role in maintaining proper posture, stabilising the spine, and facilitating movement. Let’s take a look at each core muscle’s function:
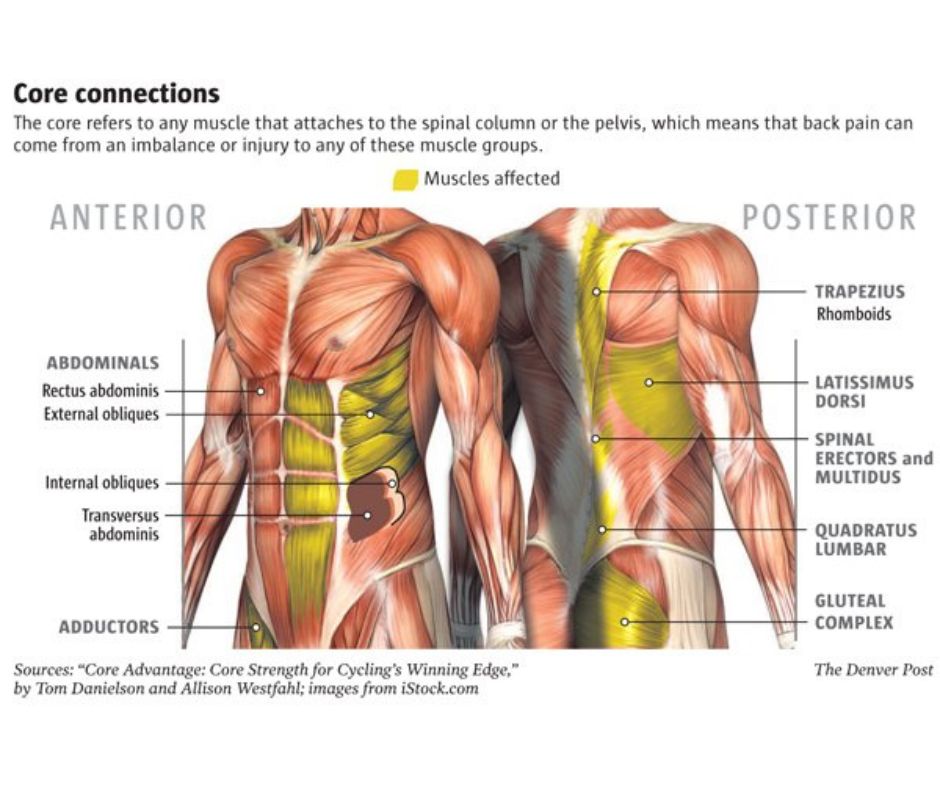
Rectus abdominis
This muscle is located in the front of the abdomen and is commonly referred to as the “six-pack.” Its primary function is to flex the spine and bring the ribs and pelvis closer together.
Obliques
The obliques are located on either side of the rectus abdominis and play a crucial role in rotational movements of the trunk. They also help to stabilise the spine and maintain proper posture.
Transverse abdominis
This muscle is located deep within the abdomen and wraps around the spine like a corset. Its primary function is to provide stability to the spine and pelvis.
Erector spinae
The erector spinae is a group of muscles that run along the length of the spine. They are responsible for extending the spine and maintaining proper posture.
Multifidus
This muscle is located deep within the back and runs along the spine. Its primary function is to provide stability to the spine and help with rotational movements.
Gluteus maximus
The gluteus maximus is the largest muscle in the body and is located in the buttocks. Its primary function is to extend the hip and assist with movements such as standing up from a seated position and climbing stairs.
Pelvic floor
The pelvic floor is a group of muscles that support the pelvic organs and help control bladder and bowel function. Strengthening these muscles can help prevent urinary incontinence and other pelvic floor disorders.
One excellent way to strengthen your core muscles is Pilates. Their controlled movements, focused breathing, and precise alignment help improve strength, flexibility, and posture.
Over time, and with consistency, Pilates will help improve alignment, stability and strength. This in combination with your osteopath will help reduce risk of injury and improve mobility.
Stay tuned for more about core strength and some powerful exercises that you can do from the comfort of your home in a future blog.
For more information on how you can incorporate strength building exercises and osteopathic techniques into your Pilates practice, click here
