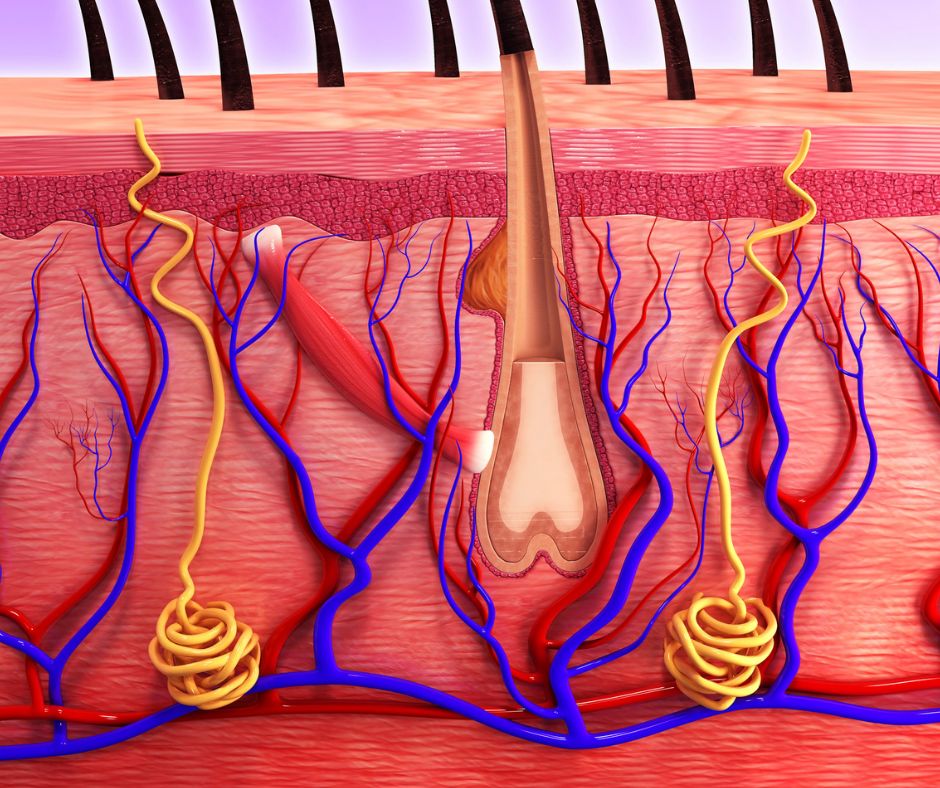
The skin, the largest organ of the human body, serves as an incredible protective barrier with a wide array of vital functions. Its role goes far beyond aesthetics, as it plays a significant role in maintaining homeostasis and overall health.
Here, we will explore the functions of the skin and its relevance in osteopathy.
1. Protection
One of the primary functions of the skin is to shield the body from external threats, including physical, chemical, and microbial agents.
The epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin, acts as a waterproof barrier, preventing excessive water loss and blocking harmful substances from entering the body. Additionally, the skin’s acidic pH inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria and fungi, further protecting against infections.
2. Temperature Regulation
The skin assists in maintaining a constant body temperature through thermoregulation. When the body overheats, the skin dilates blood vessels, allowing more blood to flow to the skin’s surface and facilitating heat dissipation through sweating.
Conversely, in cold conditions, blood vessels constrict to minimize heat loss, and hair on the skin stands erect to trap heat.
3. Sensation
The skin is rich in nerve endings, making it a vital sensory organ. It allows us to perceive various sensations such as touch, pressure, temperature, and pain.
These sensations help us interact with our environment, avoiding potential dangers, and experiencing the world around us.
4. Synthesis of Vitamin D
The skin plays a crucial role in the production of vitamin D, an essential nutrient for bone health. When exposed to sunlight, the skin synthesizes vitamin D from cholesterol. Adequate levels of vitamin D are essential for calcium absorption and maintaining strong bones and teeth.
5. Immune Defense
The skin is a part of the body’s immune system, acting as the first line of defense against infections. Specialized immune cells within the skin, such as Langerhans cells, detect and neutralize foreign invaders, preventing them from causing harm.
- Excretion
Through sweat, the skin eliminates waste products, such as urea and ammonia, from the body. This process aids in maintaining a healthy balance of electrolytes and fluid levels.
- Blood Reservoir
The skin’s vascular network, particularly in the dermis, can hold a considerable volume of blood. During times of physical exertion or injury, blood is redistributed from the skin to essential organs and muscles, helping to maintain blood pressure and overall circulation.
The relevance of the skin in osteopathy
Osteopathy is a holistic approach to healthcare that focuses on the musculoskeletal system’s interconnections with other body systems, including the skin.
Osteopathic practitioners recognize that the skin’s health and function can impact the body’s overall well-being and vice versa. Here are some ways in which osteopathy acknowledges the significance of the skin:
1. Integration of Soft Tissues
Osteopathic techniques involve gentle manipulation of soft tissues, including the skin, to improve blood flow and lymphatic drainage. This can aid in tissue healing, reduce inflammation, and promote overall tissue health.
2. Visceral Manipulation
The skin overlying internal organs can provide valuable information to osteopaths during visceral manipulation. Changes in skin texture, temperature, or sensitivity can indicate potential issues within the underlying organs.
3. Pain Management
Osteopathic treatments may address musculoskeletal pain and its referral patterns, which can manifest as skin sensitivity or discomfort. By targeting the underlying musculoskeletal imbalances, osteopaths aim to alleviate associated skin-related symptoms.
4. Circulatory Enhancement
Osteopathic techniques that promote vascular health, such as myofascial release, can indirectly benefit the skin by improving circulation and nutrient delivery to the skin’s cells.
5. Stress Reduction
Osteopathy emphasizes the body’s innate ability to heal itself. By reducing physical tension and stress in the musculoskeletal system, osteopathic treatments may positively impact skin conditions exacerbated by stress, such as eczema or psoriasis.
Final Thoughts
The skin’s multifunctional role is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. From protection against external threats to aiding in temperature regulation and vitamin D synthesis, the skin is truly remarkable.
In osteopathy, the skin’s health and function are considered important factors in understanding and treating various conditions. By incorporating skin assessment and gentle manipulation in their treatments, osteopathic practitioners can provide comprehensive care and support the body’s natural healing processes.
Remember, if you have any specific skin concerns or medical conditions, always consult with a qualified healthcare professional, such as an osteopath or dermatologist, for personalized advice and treatment.